Rova Validation Quick Reference Guide
These are the steps covered by this guide:
Selecting pathway(s) to validate
This assumes the user is already familiar with the Pathfinder application. Details of navigating Pathfinder can be found here: Luna User Guide. This covers using the dashboard grid, filtering & searching.
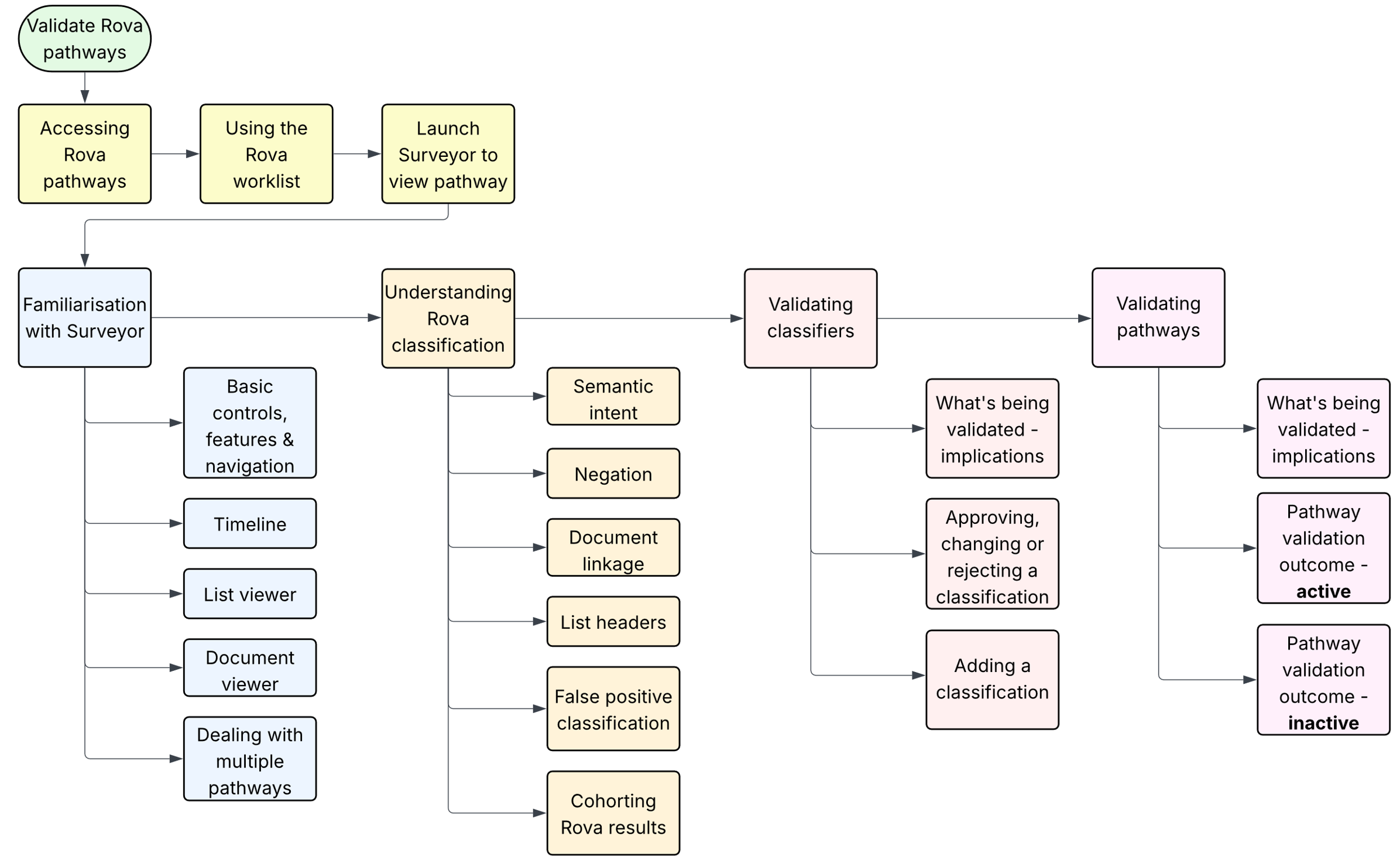
The only additional requirement for Rova is to select the Rova view from the view selection drop-down menu. It is crucial that validating Rova pathways commences from the Rova worklist, as this is how the validation outcome – the acid test of whether Rova has got its recommendation right or not – is linked to the Rova cohort;
Rova pathways are accessed either from the Rova analysis view, or the Rova RTT view. If unsure which to use, please take advice from your Trust lead or from MBI directly.
Whilst in the worklist, further filtering & sorting is possible to refine the subset of pathways being validated. A useful Rova dimension is the qualifying document – sorting for example by file created date will show the pathways that have newly qualified for the cohort.
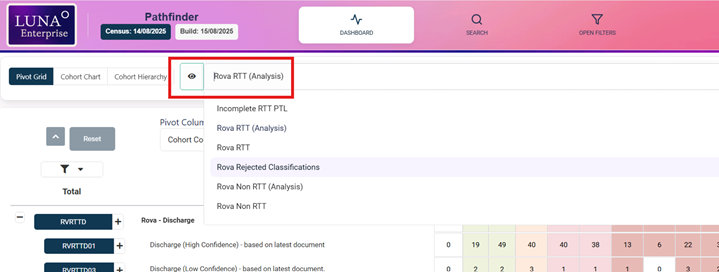
Launching Surveyor
Surveyor is launched by clicking on the magnifying glass icon for the pathway to be validated;
Navigating Surveyor
Surveyor will always open with the qualifying document highlighted in the timeline and loaded in the document viewer. Clicking on other documents in the timeline, or in he document list will load them into the document viewer.
The timeline has a number of controls to enable more or less detail;
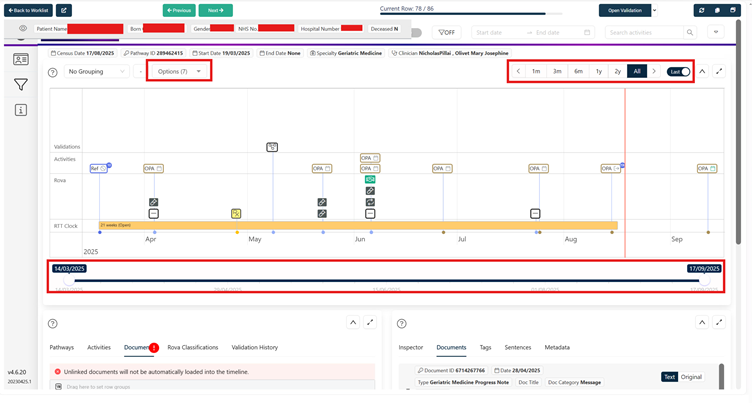
- detail toggle
- first/last xx months of the pathway
- Slider bar to zoom in/out
The first task in validating Rova pathways is to check the qualifying document is correctly linked to the pathway. Conduct the following checks between the document and pathway;
- Does the specialty & clinician match (note the clinician could legitimately be different, but if they’re the same it is highly likely it is a correctly linked document)
- If there are other documents on the main pathway, check others for reference to the clinical condition being managed & confirm the condition in the qualifying document is the same
- Does the document precede the current pathway period? It does happen occasionally & obviously is not relevant to the validation if it does.
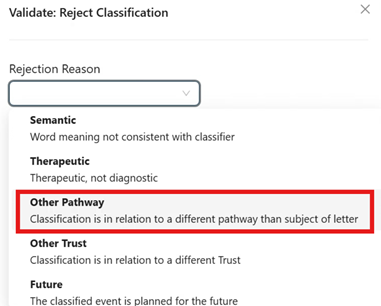
If the document is incorrectly linked to your pathway, follow the reject classification workflow set out below
Validating Rova document results
The primary classifier – each Rova cohort has a primary classifier that is intuitive & directly linked to the cohort’s description e.g. the medication classifier is the primary classifier for the medication cohort. The only variation for this is for active monitoring where the due date classifier is the primary. A typical active monitoring qualifying document will contain classification like this;

The due date classifier is the primary classifier and in this example has recognized “in about 6 months” as the potential active monitoring decision.
Negating classifiers – If there are sentences in the qualifying document that contra-indicate the primary classifier, these should be validated. These may already be classified sentences, but could also be ones Rova has missed. It is often these missed classifications that cause false positive qualification for the Rova cohorts, so we rely on feedback to refine the algorithms to ensure these are classified in future. Use the "adding classifications" instructions.
Validating the Rova Classification
In the document viewer, hovering the cursor over the classifier icon will open the validation dialogue box. Firstly confirm your validation decision accurately reflects the classifier description (or ‘semantic intent’ – See 'links to other information' section)
Approving, rejecting or changing a classification:
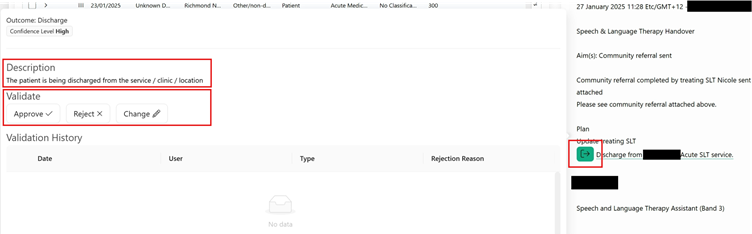
Hover your cursor over the classifier icon in the document viewer to select the validation option. Follow the on-screen instructions for reject or change & click on save when prompted. On saving, all validations are submitted automatically to the LUNA database. A confirmation message will be briefly displayed in the top right corner of the screen for all validations.
Note - if you think the classified document does not belong on the pathway you are validating, select the rejection option "Other pathway" from the drop-down (see below). This will flag a potential document linkage issue to the Rova team.
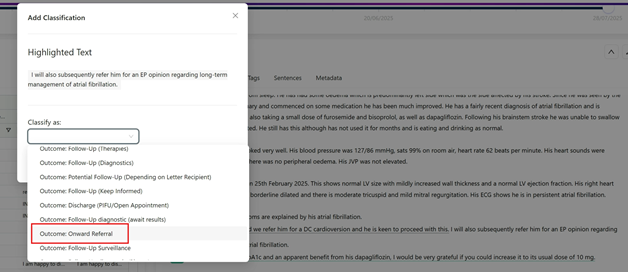
Adding a classification missed by Rova
To add a classification where Rova has missed something, select the full sentence, including any list headings that might give context to the sentence.

In this example, an onward referral is indicated, but has not been classified by Rova. Right click on the highlighted text & select the appropriate classifier from the resulting list. Click save & your suggestion will be saved to the database. The Rova team review all classifier validation & adjust the algorithms accordingly
Although it is not yet possible to “un-add” a classification if you change your mind, we would rather users submitted too many rather than opting not to add anything. Rejected/approved/changed validated classifications can all be re-validated by repeating the process above. The validation history within the validation screen will confirm the latest iteration.
To be clear, Rova does not operate 'unsupervised learning'. All user feedback via this classifier validation process is reviewed by the Rova team before any changes are made to the algorithms
Validating the Pathway
The pathway should be validated in accordance with local validation guidance and Access Policy. Use all available information in Surveyor and as required, other sources. Once a decision has been made, apply any corrections necessary to the pathway in the source PAS/EPR.
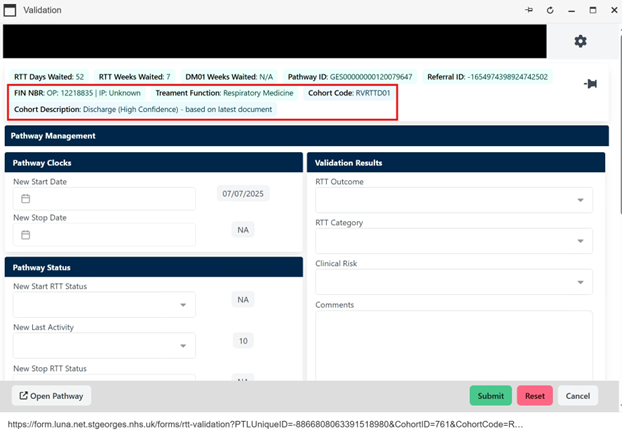
Record the validation outcome in LUNA using the form found here:
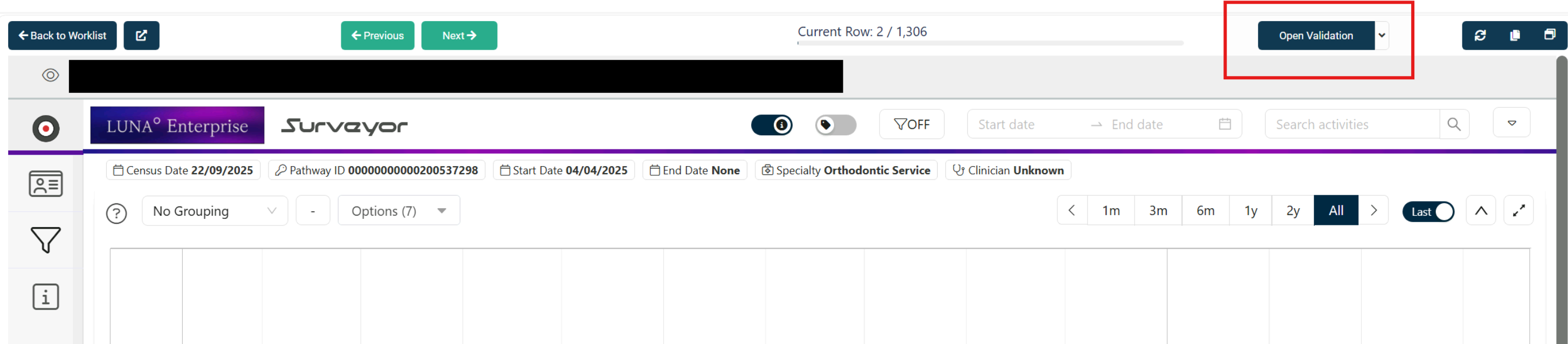
The highlighted section in the pathway validation form gives confirmation that the outcome will be linked to the Rova cohort:
Complete the form & save. From there, either return to the dashboard, or load the next pathway into Surveyor. These are the respective buttons;
Dealing with multiple pathways
Surveyor can on occasion load with more than one pathway presented in the timeline. This is because the document that qualified the pathway for the Rova cohort can also be linked to another pathway by way of the specialty/dates linkage method described in the FAQs.
Note that patients can legitimately have concurrent open pathways in the same specialty, so on occasion, this linkage method could link a document that relates to a different condition to that being managed by the pathway being validated.
Pathways can also be added to and removed from the timeline by selecting the (using the checkbox) from the pathway list in the list viewer window – note that the pathway with no checkbox is the pathway loaded from the Pathfinder worklist;
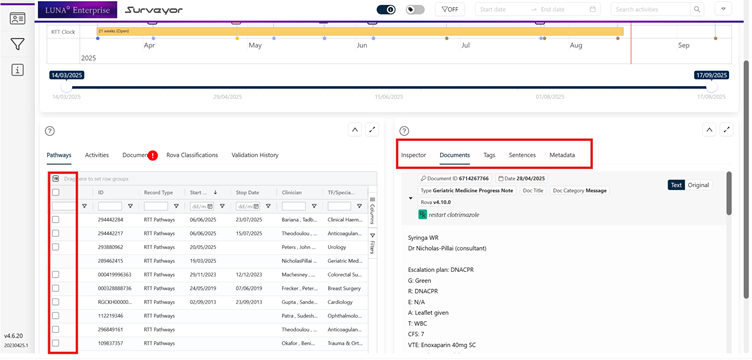
As other pathways are added to the timeline, so are all activity and documents associated with those pathways in addition to those already there linked to the 'main pathway'.
Using other pathway data in LUNA
Other related pathways can be added to the timeline as instructed above. Related specialties and overlapping dates are often clues that other pathways have been started incorrectly. Adding a pathway to the timeline will add all linked documents and activities.
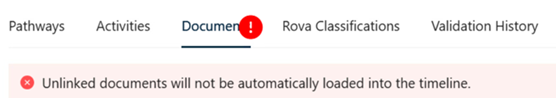
Unlinked documents: The document list header can have a red exclamation as per the image below. This means there are documents for the patient that have not been linked to any pathways. It is worth scanning the list & for any where the specialty or date may be relevant, bring them into the timeline using the checkbox in the list.
The location of the qualifying document can influence the outcome of the validation. If there is subsequent documentation and/or activity, the outcome is less likely to be a clock stop based on the Rova recommendation. Cohorting in Pathfinder takes care of document location, with some cohorts allowing the qualifying document not to be the latest on the pathway, or related to the latest activity.
Links to other information
Document scope
The document extraction process means that Rova can generally process any digital document from a Trust’s document store. There are numerous file types – PDF, DOC, TXT, RDF etc as well as document types – clinic letters, PAS comments, internal clinical notes, proforma, summaries. All of which are standardised through the extraction process which means that regardless of type/content/format, Rova is always processing the same thing – text.
Generally, Rova is deployed with scope set at a fixed time period, for example the last 5 years worth of documents at initial deployment, and all new documents from then on. The decision about timescale is made early in a deployment and generally seeks a compromise between inclusiveness and the practicalities of storage space and processing time.
As a general rule, Rova only covers documents in a Trust’s central document repository – its EPR. There can be additional documents in specialty specific systems – Medisoft for Ophthalmology, Tomcat for Cardiology, Infoflex for cancer services to name but a few. A default deployment would not typically include these, although additional connections can be made available.
Rova categorises documents into a variety of types. All can offer narrative that can be classified, although by definition some will yield more positive language matches than others. In general terms, external ‘formal’ documents that are written in long-hand language with accurate punctuation are easier to classify than internal ‘note’ type documents that tend to be heavily abbreviated, scantily punctuated and acronym heavy. Rova can and does still classify these, and there is certainly value in making Rova’s scope as broad as possible, but users should be aware of the challenges faced by the differing writing styles.
These are the categories of documents that form the basis for Rova’s scope;
Table 1: Rova document categorisation
| Document Category |
|---|
| Clinic letters |
| Community documentation |
| Diagnostic results |
| Maternity documentation |
| MDT documentation |
| Notes |
| Nursing documentation |
| Other/non-definitive |
| Pharmacy documentation |
| Referral letters |
| Messages/PAS comments |
| Admitted patient discharge documentation |
| General forms & proforma |
| GP/General/Patient letters |
| ED other documentation |
| ED discharge summary |
Semantic intent
Semantic intent describes the classifier’s purpose. As already described, Rova is looking to see if a single sentence matches a language pattern, so is not looking at the context within the document or within the wider pathway. The semantic intent defines what specifically the language patterns have been taught to look for, regardless of what else is seen in the document.
To illustrate, two examples using the Outpatient Procedure classifier, for which the semantic intent is ‘The patient underwent an intervention and/or procedure in clinic (today) that was in addition to the consultation’;
Definitive treatment – the patient has undergone a steroid injection that from an RTT perspective is definitive and would stop the clock:

Symptoms management – this patient’s RTT clock will still be ticking as they have been referred on for consideration of a more definitive intervention:

Rova is correctly identifying that a procedure has been performed in both cases, so if a user was validating the classification, they would approve this. Rova has done its job correctly as cannot be expected to ingest the context within which the procedure sentence was written.
A typical LUNA user will be vastly experienced in managing pathways, referrals and the wider context of patient care, so when looking at a Rova classification will rightly & instinctively be immediately looking at the meaning of the classification in the context of the patient as a whole. Users should understand that Rova cannot do this and therefore they should divorce the classified sentence from the wider context.
Users should always maintain focus on the classified sentence rather than the wider pathway or document. They may well have arrived at the document from a cohort for example that contains potential clock stops so would be expecting to see confirmed definitive outpatient treatments in this example. On face value, the symptoms management document would be rejected as it is not definitive, but on closer inspection both examples meet the semantic intent of the OP procedure classifier and so should be validated as such.
LUNA has an additional layer of business rules to apply to Rova classifications that allow some context to be applied to the classified documents – cohorting.
Cohort hierarchy
Rova cohorts are built in a way that a pathway can only qualify for one at a time. For example, a patient seen in Pain Management & receives a steroid injection as a definitive treatment, and also put onto PIFU can classify for both the PIFU and OP Procedures cohorts.
In general terms, the hierarchy is based on accuracy of the classifier, but can also utilise softer information. In this example, outpatient treatment could be definitive, or could be to manage symptoms whereas PIFU can only really be one thing, so is the cohort selected for this pathway.
The hierarchy in use currently is:
| BuildOrder | CohortCode | CohortDescription |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | RVRTTD01 | Discharge (High Confidence) - based on latest document |
| 2 | RVRTTD03 | Discharge (Low Confidence) - based on latest document. |
| 3 | RVRTTD02 | PIFU - based on latest document |
| 4 | RVRTTD01d | DNA Discharge - based on latest document |
| 5 | RVRTTD04 | Negated Discharge (discharge & follow up in same document) - based on latest document. |
| 6 | RVRTTM01 | Medication - document anywhere on the latest pathway period |
| 7 | RVRTTD08 | Transferred Care - to another provider for clinical or social reasons - based on latest document. |
| 8 | RVRTTD01h | Discharge (High Confidence) - based on any document after the latest activity with no subsequent documents indicating pathway continues. |
| 9 | RVRTTD01dh | DNA Discharge - document anywhere on latest pathway period with no subsequent documents indicating pathway continues |
| 10 | RVRTTD02h | PIFU - based on any document after the latest activity with no subsequent documents indicating pathway continues |
| 11 | RVRTTD07 | Negative Diagnostic Outcome - based on latest document |
| 12 | RVRTTD05b | Active monitoring - based on the latst document on the pathway period |
| 13 | RVRTTD09b | Surveillance - either at this Trust, in primary care or with a national screening programme - based on latest document |
| 14 | RVRTTD13 | Follow-Up Diagnostic Due Date - document anywhere on the latest pathway period |
| 15 | RVRTTD05 | Active monitoring - document anywhere on the latest pathway period |
| 16 | RVRTTD09 | Surveillance - either at this Trust, in primary care or with a national screening programme - document anywhere on the latest pathway period |
| 17 | RVRTTD12 | Negative Diagnostic Result (No Follow-Up) - based on latest document |
| 18 | RVRTTD12a | Negative Diagnostic Result - based on latest document |
| 19 | RVRTTD12f | Negative Diagnostic Result - document anywhere on the latest pathway period |
| 20 | RVRTTF01 | Follow up activity required - based on latest document. latest activity is an OP Appointment |
| 21 | RTTOPTRT01 | Outpatient Procedure - OP procedure treatment took place in clinic over and above the consultation |
| 22 | RTTOPTRT02 | Medical Device - Device issued in clinic over and above the consultation |
| 23 | SUBSREF01 | Pathways on the RTT PTL cohorts where there is a subsequent referral on the same patient and treatment function in any status OR any other open referral on the same patient and treatment function |
| 24 | RVRTTD10a | Pathways currently on the RTT PTL cohorts where the latest OP attendance on the pathway is "Discharged from Consultant's Care" and a linked document exists on the pathway. Document can be linked by any method. |
| 25 | RVRTTD10b | Pathways currently on the RTT PTL cohorts where the latest OP attendance on the pathway is "Discharged from Consultant's Care" and a linked document DOES NOT exist on the pathway. |
| 26 | RTTOUTC01 | Pathways on the RTT PTL cohorts where the latest appointment on the pathway has a missing outcome |
| 27 | RTTOUTC02 | Pathways on the RTT PTL cohorts where the latest appointment on the pathway has an Outcome of Attendance in Group A (ADD DESCRIPTION LOCALISATION IN dbo.ViewCohortLink or Post Deployment) |
| 28 | RTTOUTC03 | Pathways on the RTT PTL cohorts where the latest appointment on the pathway has an Outcome of Attendance in Group B (ADD DESCRIPTION LOCALISATION IN dbo.ViewCohortLink or Post Deployment) |
| 29 | RTTNOATT02 | Pathways on the RTT PTL cohorts that have no OP attendances, IP admissions or open IPWL entries linked to the pathway |
| 30 | RVNODOC01 | Pathways on the RTT PTL cohorts that have no documents linked to the patient record |
| 31 | RVNODOC02 | Pathways on the RTT PTL cohorts that have no documents linked to the pathway record |
| 32 | RVCLASS01 | Pathways currently on the RTT PTL cohorts that have a document classified by Rova as Rova as "Discharged" (High/low Confidence). The document date is AFTER the pathway start date/referral received date |
| 33 | RVNOCLA01 | Pathways on the RTT PTL cohorts that have documents linked to the pathway, all of which have no positive classifications |
Document List headers
List headers vary significantly between Trusts & even between services within Trusts. Essentially a list header is a section title either in a template type document or a letter document. Typically, list headers are used at the start of the narrative to summarise the patient contact & cover;
- Clinical history
- Investigations to date
- Medications
- Management plan (from this contact)
These lists can be a mine of useful information captured in short-form & not always in the body of the document. Equally, they can be a challenge for Rova as the list header can completely change the meaning of the classified sentence. For example;
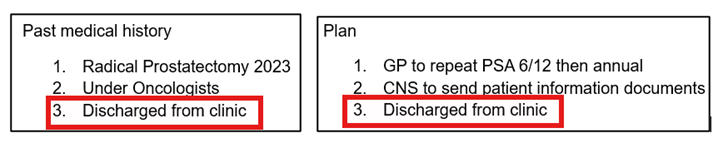
In both of these, the classified text is identical, but their meaning is completely changed by the list header – from a historic inference that the patient was discharged from Oncology to a clear positive discharge from Urology.
Negation
A typical document will describe multiple actions required for a patient, and so can be classified by multiple classifiers. Negation is a business rule built into the cohorting process that effectively allows a particular classifier within a document to 'trump' other classifiers in the same document.
Cohorts are built around 'primary' classifiers - the discharge cohort's primary classifiers for example are the discharge and dscharge - rerefer classifiers. The basic principal of negation is to look for any other classifier that may contradict the primary classifier and if found, the logic will exclude that pathway from the cohort.
The following table shows the negating classifiers for the core RTT Rova cohorts (at the time of writing). Note that subsidiary cohorts (suffixed with a/b/h/d) use the same negation rules;
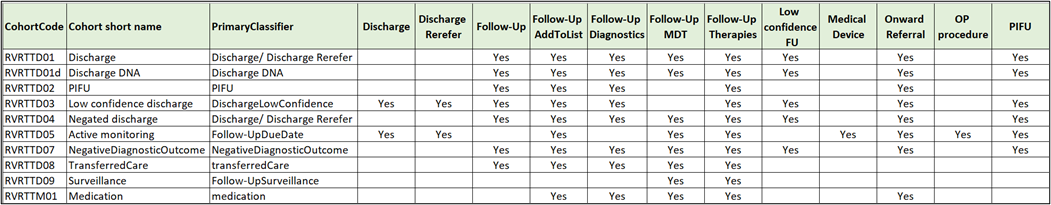
To illustrate, if a document is classified as follow up - therapies, it will negate all of the clock stop primary classifiers. Another example is where the document indicates active monitoring (6 month follow up) but is also classified as requiring a diagnostic - the diagnostic request would negate the active monitoring;

Another example - Rova has classified a good outpatient procedure which would normally be cohorted as an RTT clock stop, but the patient has also been referred on to another service to take over care. The onward referral negates the procedure, and the pathway is excluded from the OP procedure cohort

FAQs
Why are there multiple classifications of the same sentence?
This is predominantly associated with the many different types of follow up classification. Core to this is the high confidence follow up classifier looking simply for language that confirms that an intervention of some sort is required in the future. This means there can be overlap between this and other classifiers.

This classifies for add to list, picking up the ‘listed for ACL reconstruction’ and for a high confidence follow up as the ‘listed for’ term is connected to the management header ‘Plan’

Similarly this example meets the definition of both the high confidence follow up and the diagnostic classifiers

This example has a high confidence follow up paired with the due date classifier. The follow up appointment is obviously classified, but also the ‘6 months’ as the sentence confirms a time period for the follow up

This example has a third classifier – the low confidence follow up in white. The low confidence follow up is designed as a catch-all for any possible hint of a follow up action being required, in this case the ‘we will arrange’ phrase. These classifiers were designed primarily to negate discharges but unfortunately we are not yet able to use them selectively, so they can be ignored where other follow up classifiers exist.

Due date can be triggered by any form of high confidence follow up – in this case, the physio timeframe and the appointment have both been classified

One final variation – 2 follow ups and 2 due dates. This is actually a high confidence follow up plus a ‘shorthand’ follow up. The shorthand version uses the list header in combination with the term ‘follow up’, whilst the high confidence follow up classifies the sentence in isolation.
Rova casts its net wide in an attempt to capture as much variation in language, which it does well. What you see here is the overhead of when the algorithms overlap, normally because of shorter, less grammatically correct sentences.
I can’t see an icon for active monitoring.
Rova doesn’t yet have a classifier that looks for language specifically referencing active monitoring, but instead uses the ‘due date’ classifier with any phrase implying a 6 month or longer lead time for the follow up appointment qualifying the pathway for the active monitoring cohort. An active monitoring classification may then look something like this;

Why am I seeing documents on my pathway that are not relevant?
Documents are not generally linked to pathways in an EPR system – there’s no real operational or clinical need to do this, so we have to create linkage in LUNA. In order of precision, LUNA does this by (assuming the document can be linked to a patient);
a) Using a direct link to the pathway
b) Document is linked to an activity, which in turn is linked to a pathway
c) The document is linked to the same specialty as the pathway & the document date is within the pathway period’s start (& stop if applicable) date.
This last method can, when a patient has more than one concurrent pathway for different conditions, lead to the document being incorrectly linked to your pathway. These should be flagged to the Rova support team be rejecting the primary classification;

The pathway I’m validating should remain active, meaning the Rova recommendation was wrong. Isn’t Rova supposed to be finding clock stops?
Rova’s primary objective for the RTT PTL is to find clock stop events/decisions from documents. However, the nature of the beast is that there are infinite combinations of language & pathway events means there will inevitably be scenarios that present as false positives i.e. where Rova has recommended a clock stop, but human validation finds something Rova hasn’t.
The Rova team aspire to Rova being correct for 90% + of pathways that qualify for cohorts. Experience so far suggests that this is generally the case for discharge & PIFU cohorts, but less so for active monitoring, surveillance and outpatient treatments. For these, we see results anywhere between 60-90% which although is below par in terms of our target, still represents a sizeable efficiency gain compared to manual validation. Where this scenario is seen, simply validate the pathway as active in order to flag to the Rova team
Why has Rova classified a discharge for an inpatient discharge, not a pathway discharge?
We have developed the Rova discharge algorithm to spot ‘short-form’ language as well as the more descriptive language typically found in clinic letters. This is to broaden the scope of Rova to documents such as notes, messages & comments where we do find considerable volumes of positive matches.
Discharge summaries do contain usable information in relation to pathway management, most notably with follow up arrangements or instructions; “Follow up: not required” & similar. This makes discharge summaries a viable document type for Rova, but the overhead on occasion is ward or hospital discharges are occasionally classified by the short-form elements of the discharge classifier.
How does a low confidence discharge differ from a high confidence discharge?
A low confidence discharge is typically where the language suggests the patient is being discharged from a specific service or clinician, but their pathway may well continue with another service. This could be discharge from a 2WW pathway to a routine pathway, or from a consultant's care to the specialist nurse or AHP.
Often a sentence will classify as both a high and a low confidence discharge which although is not a bug, is something that needs refining. The user should be aware of the cohort they are validating from, so this shouldn't confuse the validation. Ultimately Rova is directing the user toward a potential discharge, but the presentation of the classification does need attention.
What is a negated discharge?
These are high confidence discharges, but where Rova has also found a low confidence follow up - where there is a 'hint' of something else in the qualifying document - typically a request for someone else - the GP, the patient or another clinician - to undertake an action of some kind. Often these can be requests for actions in primary care, which would not negate the discharge from the secondary care service, but to be on the safe side, these are presented as low confidence so that the user knows to look for and verify these other actions.
There is no need to validate the low confidence follow up in Surveyor, unless this has been specifically requested.
Glossary - TBC
Timeline
List viewer
Document viewer
Linkage/document linkage
High/low confidence
Classifier